Insider trading has intrigued investors, authorities, and the public for a long time. This illicit conduct includes buying or selling shares using secret information that gives some people a financial benefit. Insiders have access to forthcoming corporate statements, financial results, and key events that could affect a company’s share price. Hence, there should be a strong emphasis on these activities and the actions related to it.
Insider trading punctures open and egalitarian markets and the strength of the financial system. In this blog, we shall discuss insider trading’s definition, manifestations, noteworthy examples, and legal framework to prohibit and punish it. We strive to increase insider trading knowledge and its repercussions to create a fairer investing environment.
What Exactly is Insider Trading?
Insider trading is the illegal purchase and sale of securities like bonds or stocks based on non-public company information. Managers, directors, and employees with access to sensitive insider information work there. Insider trading guidelines prioritize fairness and leveling the playing field. Using non-public information for personal gain affects financial market honesty and openness.
Insider trading can manipulate stock prices, deceive investors, and damage system credibility. To deter and prosecute insider trading, international regulatory bodies like the SEC have rigorous laws and penalties. These measures protect investor interests, market integrity, and financial market trust.
How does an Insider works?
Who are Insiders?
A company insider has exclusive, non-public knowledge about the company due to their work or relationship. Insiders include top executives, directors, officials, and workers with sensitive facts that could materially impact the company’s securities. Insiders have insights the public doesn’t, allowing them to make smart financial judgments. Remember that insiders must act in the company’s and shareholders’ best interests and that trading on inside information is illegal.
How Does Insider Trading Work?

Insider trading lets people with access to confidential information benefit. Executives and workers might have access to sensitive and vital information about a company through their jobs or contacts. Mergers and acquisitions, financial performance, regulatory clearances, product advances, and other information could significantly affect the company’s stock price.
Insiders use non-public information to make decisions about buying or selling securities. They execute transactions through brokerage accounts or other channels to profit from the projected price movement based on privileged information. They may buy or sell stocks through relatives, friends, or offshore accounts to obscure their relationship. Insiders might profit from public information by selling their interests at a higher price or avoiding losses before the stock price declines.
Types of Insider Trading
Classic Insider Trading: Using key non-public information to trade assets.
Tipper-Tippee Trading: Insiders share private knowledge for trading.
Blackout Period Trading: Insider trading when some individuals are prohibited from trading.
Front-Running: Trading for clients or the company before large orders.
Misappropriation: Trading with stolen or misused confidential information.
Effects of Insider Trading?
- Insiders gain an unfair advantage, leading to unfair market conditions.
- Investors lose trust in financial market honesty and fairness.
- There is a risk of stock price manipulation and investor harm without access to secret information.
- Reducing market efficiency and transparency.
When is Insider Trading Illegal?
People are frequently accused of engaging in insider trading, which is against their fiduciary and trust duties, when they trade shares based on sensitive non-public knowledge. It becomes a crime when:
● Material Non-public Information: Trading on non-public information can dramatically alter stock prices.
● Fiduciary Duty Breach: Executives or employees fail to act in the best interests of shareholders by abusing or revealing confidential information.
● Misappropriation: Trading on stolen or unlawfully obtained confidential information.
When Is Insider Trading Legal?
If done legally, insider trading is usually fine. Permitted insider trading includes:
● Rule 10b5-1 projects allow insiders to conduct pre-planned transactions.
● Publicly available information includes regulatory filings and official declarations.
● Non-material Information: Trading on data that does not materially affect stock price or investor selections.
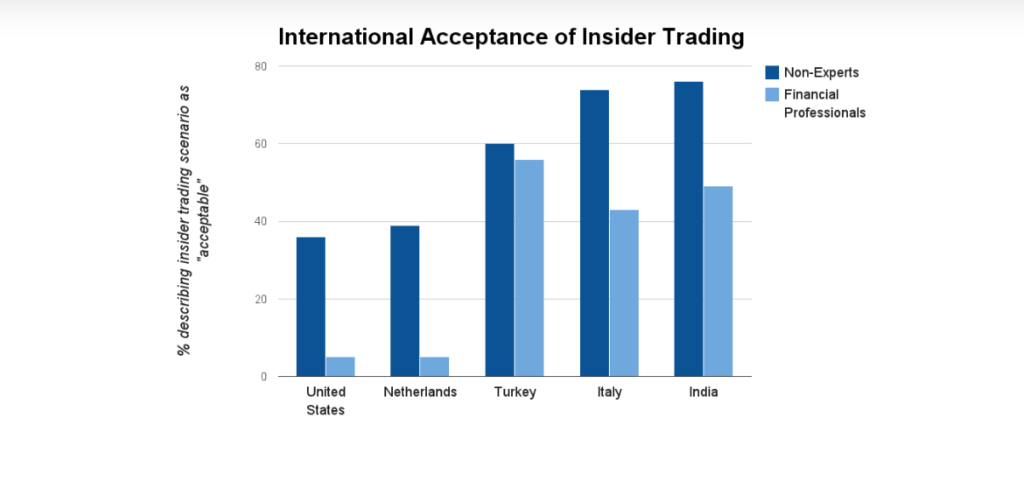
Image Source
Penalties for Insider Trading
Insider trading sanctions vary by jurisdiction and offense severity. The joint sanctions could be:
Financial Penalties: Those found guilty of insider trading may be subject to significant fines, often based on unlawful gains.
Prison: Serious insider trading offenses may result in prison terms, depending on the severity of the crime.
Restitution: Disgorgement orders may require insider traders to repay earnings.
Civil penalties may include restrictions on trading, license cancellation, or other measures.
Conclusion- How to stop insider trading practices?

Preventing insider trading involves implementing vital compliance programs and educating staff about legal obligations and repercussions. We all should encourage establishing specific policies and guidelines, monitoring trading activity, and enforcing strict information barriers. Government and corporate agencies should conduct routine audits, and foster an ethical and honest company culture to ensure that insider trading is diminished.
For more info, check out our blog.
FAQs
What makes Insider trading illegal?
When the relevant information is still secret, insider trading is prohibited and carries severe penalties, such as possible fines and jail time. Any information that has the potential to materially affect the stock price of that company is considered material non-public information.
Who is an Insider?
According to the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), an officer, director, or 10% shareholder of a company who has access to inside information about the company due to their affiliation with a principal shareholder, officer, or director of the company is considered an insider.
Should I be worried about Insider Trading?
For holders of demat accounts in India, engaging in insider trading, whether intentionally or unintentionally, can have dire consequences. The practice of trading securities based on confidential information, or “insider trading,” has raised serious concerns for regulators worldwide.
Is Insider Trading allowed in India?
It is never acceptable for a designated individual or their close associates to engage in insider trading in India. A Designated Person who purchases or sells any quantity of the company’s stock is prohibited by SEBI laws from engaging in a conflicting transaction for six months following the transaction date.



